What is SMC(Singapore Math Challenge)?
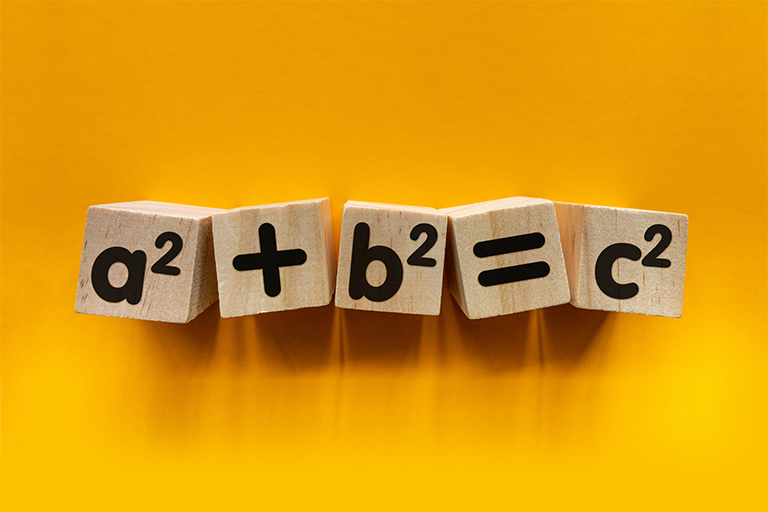
The Process
Calculator is not allowed for Primary 1–4 and allowed for grades 5-12

15 Questions × 2 Marks = 30 Marks

10 Questions × 4 Marks = 40 Marks

6 Questions × 5 Marks = 30 Marks

Program Highlights
Medal winners get physical awards; all participants receive E-certificates and performance reports. Top scorers qualify for the Singapore Math Global Finals (SMGF).
Top 8% of Participants
Next 12% of Participants
Next 20% of Participants
Next 10% of Participants
Awarded to All Participants
Full Marks + Additional Prizes
FAQS
Students from Grades 1 to 12 studying under CBSE, ICSE, IGCSE, IB, or any State Board are eligible to participate. The exam is open to students across India and internationally.
Students from Grades 1 to 11 studying under CBSE, ICSE, IGCSE, IB, or any State Board are eligible to participate. The exam is open to students across India and internationally.
The SMC follows a Singapore Math-based syllabus that blends core arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and logical reasoning. It goes beyond regular school textbooks to test students on problem-solving strategies, pattern recognition and real-world applications.
Participating in math Olympiads offers several long-term academic and cognitive benefits:
While Indian math Olympiads like IOM or IMO focus on syllabus-based assessment aligned with CBSE, ICSE, and State Boards, the SMC emphasizes international standards and problem-solving depth.
Key differences include:
To prepare effectively:
The Singapore Math Competition is typically conducted online under supervision, but formats may vary based on regional partnerships and participating centers.
You can register through your school, authorized training center, or official SMC partner in India. Individual registrations may also be accepted depending on your location.
Get Started Today
Expert mentorship, focused concept development, and consistent practice combine in this program to deliver targeted Olympiad preparation and the skills needed for academic excellence.
Join Us and See the Difference.
Copyright © The Talent Scholar